Couple of weeks back vSphere 7.0 released & if you ask me, it is a massive release with several cool features and capabilities including “vSphere with Kubernetes”. I was going through all the REST APIs introduced as part of multiple features shipped in this release and I see that this is the first release, where REST APIs are hands down dominating traditional SOAP based APIs. New capabilities have not only been exposed through REST APIs but also some of the older capabilities have provided REST API support as well. In this series of posts, I would like to introduce you these REST APIs as I did for vSphere Supervisor Cluster last week. In this post, I will touch upon new APIs introduced as part of “Virtual Machine” Management & demonstrate them using Postman client and Python.
Where do I get REST API documentation? This is available as part of H5C API Explorer itself since vSphere 6.5: H5C >> Menu >> Developer center >> API explorer or you can look documentation at VMware {code} site as well.
Since vSphere 6.5, when it comes to REST APIs with respect to VM life cycle, only minimal support was available i.e. Get, Create (POST call) and Delete VMs. With vSphere 7.0, I see there is huge progress made with respect to supporting key capabilities such as relocate, normal clone, instant clone & register VMs operations. Traditionally automating these VM life cycle ops have been challenging for several users using SOAP APIs, now with REST API support, it has drastically simpler to consume/automate these capabilities. Below is how its POST call URLs look like
Relocate ops:
POST https://{server}/rest/vcenter/vm/{vm}?action=relocate
POST https://{server}/rest/vcenter/vm/{vm}?vmw-task=true&action=relocate
Only difference between them is that 2nd API also returns task object, which will help user track the progress of the operation.
Clone ops:
POST https://{server}/rest/vcenter/vm?action=clone
POST https://{server}/rest/vcenter/vm?vmw-task=true&action=clone
Similar to relocate API, second API returns task object.
Instant clone ops:
POST https://{server}/rest/vcenter/vm?action=instant-clone
Register ops
POST https://{server}/rest/vcenter/vm?action=register
POST https://{server}/rest/vcenter/vm/{vm}?action=unregister
Note that there is no change to existing SOAP APIs for all the existing capabilities, it should continue to work fine without any impact
Let us now understand one of the APIs in more detail. Without a doubt, it should be all time famous capability i.e. vMotion (relocate).
POST https://{server}/rest/vcenter/vm/{vm}?action=relocate
Below is how payload for this API look like
{
"spec" : {
"disks" : [
{
"value" : {
"datastore" : "datastore_moid"
},
"key" : "disk key"
}
],
"placement" : {
"cluster" : "cluster_moid",
"folder" : "folder_moid",
"datastore" : "datastore_moid",
"host" : "host_moid",
"resource_pool" : "resourcepool_moid"
}
}
}
let us understand each of the parameter being passed in brief. For detailed documentation, please refer official documentation from API Explorer or from vmware {code} portal.
disks []: This spec has 2 values such as datastore and key as follows, it is required field to pass details for all the VM disks.
datastore : required: This parameter under “disks[]” should be the destination datastore for the VM disks. This should be datastore_moid and moid found using existing REST API:
GET https://{server}/rest/vcenter/datastore
sample value : “datastore-21”
key: required: this must be the disk key(s) for the VM to be migrated and it can be found using existing REST API. sample value : “2000”
GET https://{server}/rest/vcenter/vm/{vm}/hardware/disk
placement : destination spec
cluster: this should be cluster moid. This can be specified if we would like DRS to find the right host for placement. This can be optional param. moid can be found using API: sample value : “domain-c9”
GET https://{server}/rest/vcenter/cluster
folder: destination VM folder. This is optional param. moid can be found using API. sample value : “group-v4”
GET https://{server}/rest/vcenter/folder
datastore: This is under placement_spec: This is required if you want relocate VM configuration folders/files to destination. The “datastore” property briefed before above is for VM disks.
host: destination host. It is optional if cluster or resource pool is passed. sample value : “host-32”
moid can be found using API: GET https://{server}/rest/vcenter/host
resource_pool: destination resource pool. This is not required if host or cluster is specified. sample value : “resgroup-34”
moid can be found using API: GET https://{server}/rest/vcenter/resource-pool
Note that there are couple of noteworthy points wrt relocate and clone REST APIs. As of vSphere 7.0, it does not give an option to specify destination network & it does not support cross vCenter migration/clone as well . I hope in future releases, both of these key aspects will be supported through REST APIs
Let us invoke this API. I did it using both postman REST client and Python.
Postman way:
Note: In my case, I am relocating the VM from one cluster to other DRS enabled cluster. If you do not have DRS enabled cluster, you can go with passing destination host instead. I passed just enough params as shown below in Postman client but you may pass as per your requirement. 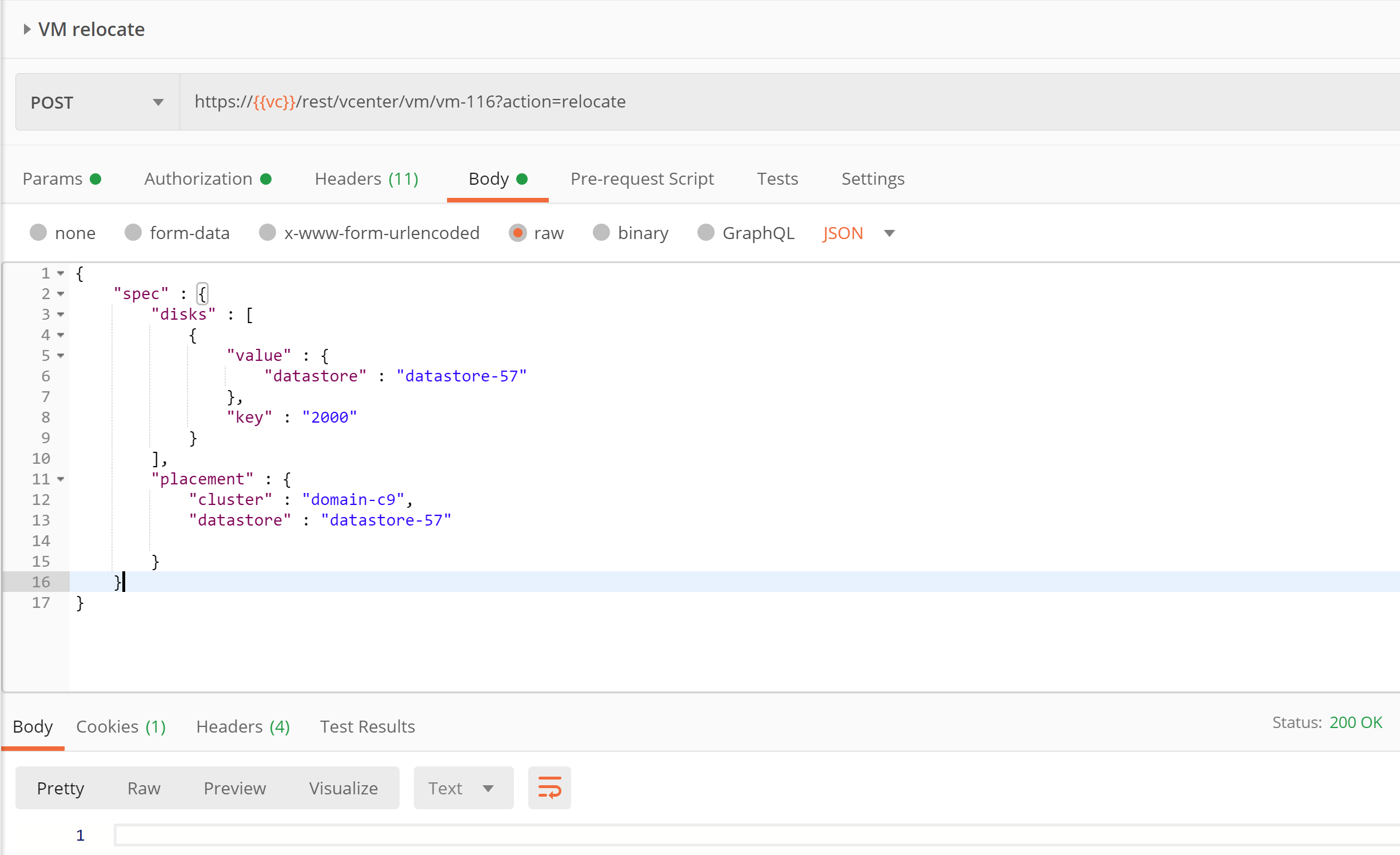
Here is the payload passed for easy copy paste.
{
“spec” : {
“disks” : [
{
“value” : {
“datastore” : “datastore-57”
},
“key” : “2000”
}
],
“placement” : {
“cluster” : “domain-c9”,
“datastore” : “datastore-57”
}
}
}
Python way:
Here is the equivalent python script for the same on my github repo. Below is how you would execute this python script 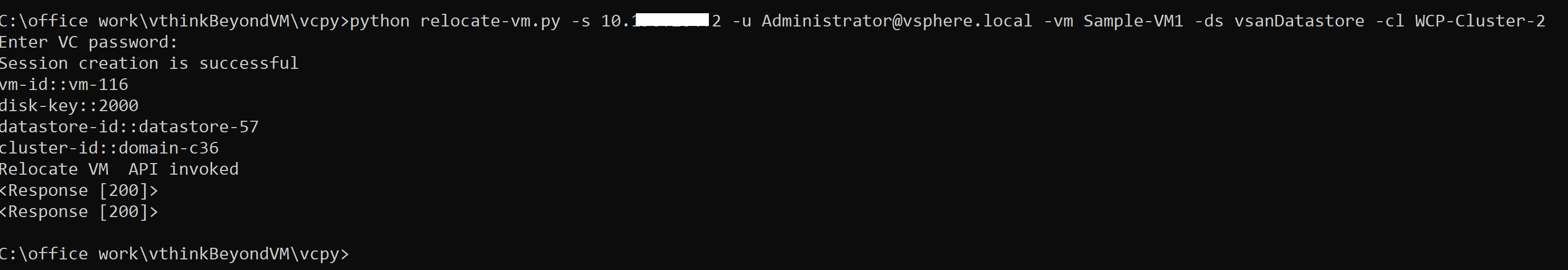
You can see API returned 200 ok response. how cool is that!
I hope you enjoyed this post. Please stay tuned for next post in this REST API series.
References:
– How to get started guide on REST APIs using Postman and python
– Introduction to vSphere Supervisor cluster APIs